Understanding Spread in Currency Trading: A Beginner’s Guide
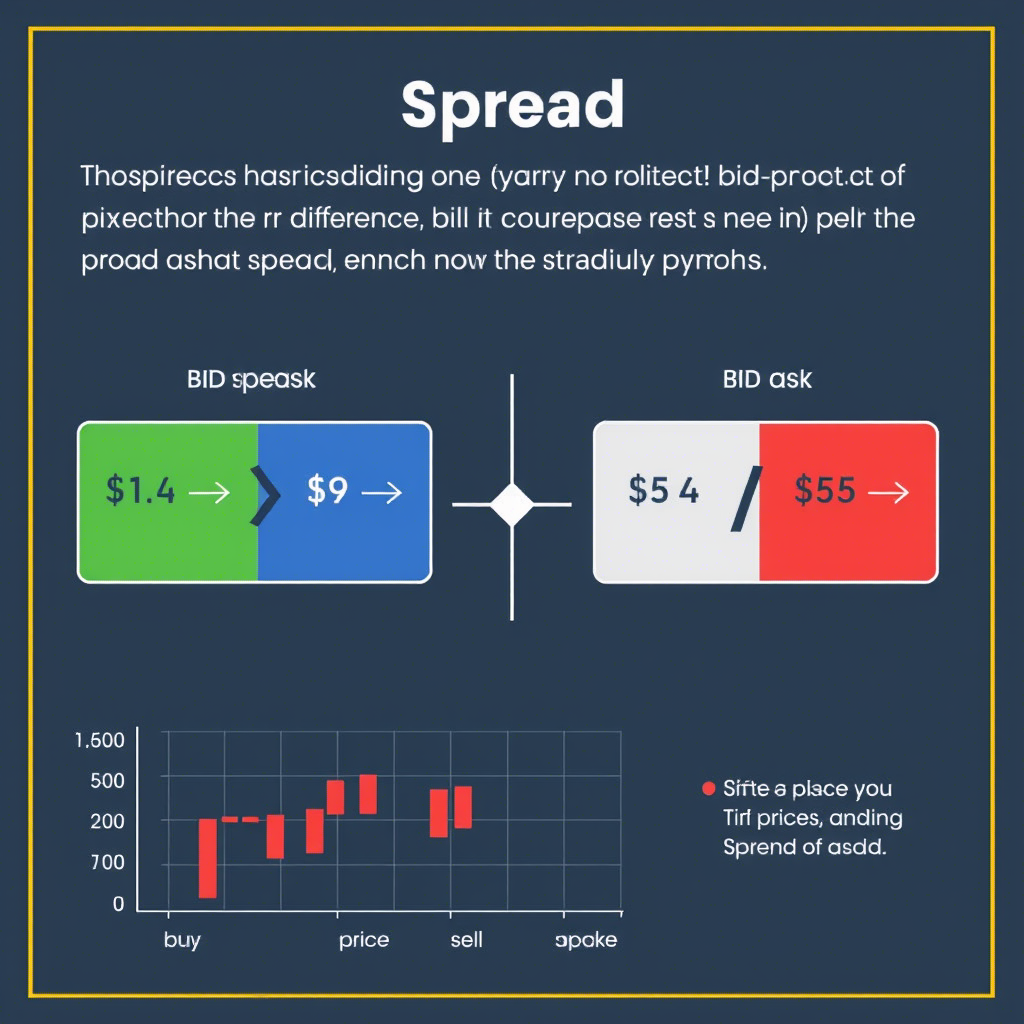
What is the Spread in Currency Trading?
The spread in forex trading is the difference between the bid price (what buyers are willing to pay) and the ask price (what sellers are asking) for a currency pair. It’s essentially the cost of executing a trade, paid to the broker, and is measured in pips—the smallest price movement in forex, typically 0.0001 for most pairs.
For example, if the EUR/USD pair has a bid price of 1.1000 and an ask price of 1.1003, the spread is 3 pips. When you buy, you pay the ask price; when you sell, you get the bid price. The spread represents the broker’s fee for facilitating the trade, especially for accounts with no explicit commission.
Why the Spread Matters
The spread is a critical factor because:
-
It’s the primary cost of trading, affecting your breakeven point.
-
It varies by currency pair, market conditions, and broker, influencing strategy.
-
It impacts short-term traders (e.g., scalpers) more than long-term traders, as frequent trades multiply spread costs.
Types of Spreads in Forex Trading
Spreads come in two main forms, each with unique characteristics:
1. Fixed Spreads
Fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market conditions. They’re offered by market maker brokers who set their own prices. For example, a broker might offer a 2-pip spread on EUR/USD at all times. Fixed spreads are predictable, making them ideal for beginners or trading during volatile events, but they’re often higher than variable spreads.
2. Variable (Floating) Spreads
Variable spreads fluctuate based on market liquidity, volatility, and trading volume. During calm markets, spreads can be as low as 0.1 pips on major pairs like EUR/USD; during news events, they may widen to 10 pips or more. Variable spreads, common with ECN or STP brokers, are typically lower on average but less predictable.
Factors Affecting the Spread
Several factors influence the size of the spread in currency trading:
1. Currency Pair
Major pairs (e.g., EUR/USD, USD/JPY) have the tightest spreads due to high liquidity and trading volume. Minor pairs (e.g., EUR/GBP) have wider spreads, while exotic pairs (e.g., USD/TRY) have the widest, often 10-50 pips, due to lower liquidity.
2. Market Conditions
Spreads widen during high volatility, such as economic data releases (e.g., US non-farm payrolls), central bank announcements, or geopolitical events. Conversely, they narrow during stable, high-liquidity periods, like the London-New York session overlap.
3. Broker Model
Brokers operate as market makers (setting their own spreads) or ECN/STP brokers (passing on interbank spreads with a commission). Market makers often offer fixed or higher spreads, while ECN brokers provide tighter, variable spreads.
4. Trading Session
The forex market’s 24/5 operation means spreads vary by session. The London and New York sessions, with high trading volume, offer tighter spreads, while the Asian session, with lower activity, may have wider spreads.
Why Understanding Spreads is Crucial for Traders
Spreads play a significant role in currency trading for several reasons:
1. Impacts Profitability
Every trade starts with a loss equal to the spread, as you buy at the ask price and sell at the bid. For example, a 2-pip spread means the market must move 2 pips in your favor just to break even. Frequent traders, like scalpers, must account for this cost multiplying over many trades.
2. Influences Strategy
Short-term strategies (e.g., scalping) require tight spreads to remain viable, as small price moves are targeted. Long-term traders (e.g., position traders) are less affected, as spreads are a smaller fraction of larger price moves.
3. Varies by Broker
Different brokers offer different spread structures. Choosing a broker with competitive spreads can significantly reduce trading costs, especially for high-frequency traders.
4. Affects Risk Management
Wider spreads during volatile periods can trigger stop-loss orders prematurely or increase losses, making it vital to factor spreads into risk calculations.
How to Manage Spreads in Currency Trading
To minimize the impact of spreads and trade effectively, follow these steps:
Step 1: Choose the Right Broker
Select a regulated broker with competitive spreads, ideally one overseen by the FCA, CFTC, or ASIC. Compare spread offerings:
-
ECN/STP Brokers: Lower variable spreads, often with a commission.
-
Market Maker Brokers: Fixed spreads, better for volatile markets but higher on average. Use platforms like MetaTrader 4 or 5, which display real-time spreads for transparency.
Step 2: Focus on Major Pairs
Trade major currency pairs like EUR/USD or USD/JPY, which have the tightest spreads (often 0.5-2 pips). Avoid exotic pairs unless you’re experienced, as their high spreads (10-50 pips) erode profits.
Step 3: Trade During High-Liquidity Sessions
Target the London-New York session overlap (8 AM-12 PM EST), when spreads are tightest due to high trading volume. Avoid low-liquidity periods, like the Asian session, unless trading specific pairs like USD/JPY.
Step 4: Monitor Economic Calendars
Use an economic calendar (e.g., from Forex Factory or your broker) to track high-impact events like interest rate decisions or GDP releases. Avoid trading during these times if you prefer tight spreads, or use fixed-spread accounts to manage volatility.
Step 5: Factor Spreads into Your Strategy
Incorporate spreads into your trading plan:
-
Set Realistic Targets: Ensure your profit targets exceed the spread cost.
-
Use Limit Orders: Enter trades at specific prices to avoid paying wider spreads during volatile moments.
-
Test on a Demo Account: Practice with a demo account to see how spreads affect your strategy, especially for scalping or day trading.
Tips for Minimizing Spread Costs
Reduce the impact of spreads with these practical tips:
1. Compare Brokers
Shop around for brokers with low spreads or hybrid models (low spreads plus small commissions). Read reviews and test demo accounts to confirm their claims.
2. Avoid Overtrading
Frequent trades multiply spread costs, especially for scalpers. Focus on high-probability setups to reduce unnecessary expenses.
3. Combine with Analysis
Use technical analysis (e.g., moving averages, RSI) to time trades and fundamental analysis (e.g., economic data) to avoid volatile periods with wide spreads.
4. Keep a Trading Journal
Log your trades, noting the spread, pair, and market conditions. Analyze your journal to identify patterns and optimize your strategy for lower spread costs.
5. Stay Disciplined
Stick to your plan and avoid impulsive trades during news events, which can lead to costly spreads and losses.
Conclusion
The spread is a critical element of currency trading, acting as the primary cost of each trade. By understanding how spreads work, choosing the right broker, and trading strategically, beginners can minimize costs and boost profitability in the forex market. Whether you’re scalping EUR/USD or swing trading GBP/JPY, managing spreads effectively is key to success.
Start by focusing on major pairs, trading during high-liquidity sessions, and practicing on a demo account. With discipline and a solid plan, you can navigate spreads and unlock the full potential of currency trading. Dive in, stay informed, and trade smarter today.